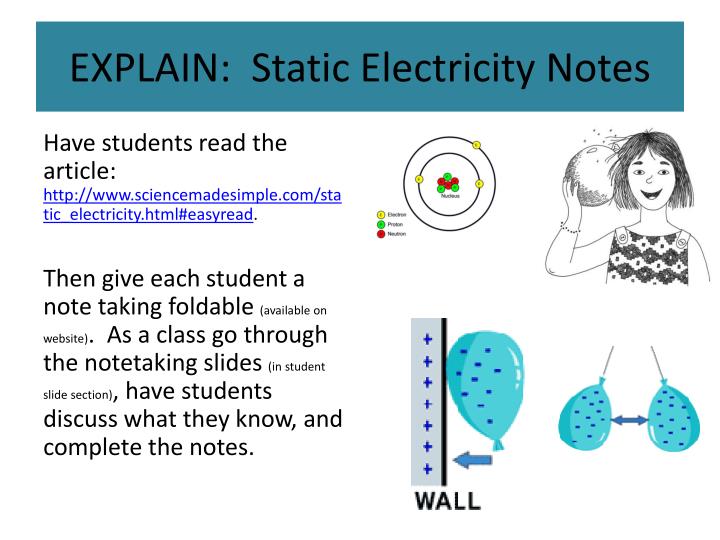
Explain Static Electricity . It is called “static” because the displaced. basic principles of electrostatics are introduced in order to explain how objects become charged and to describe the effect. Some of the electrons are transferred across. Accumulating a charge requires the transfer of electrons from one object to another. The result of an imbalance of this “fluid” (electrons) between objects is called static electricity. Typically, objects are neither positively or negatively charged—they experience an overall charge of zero. static electricity can be a nuisance or even a danger. The energy that makes your hair to stand on end can also damage electronics and cause explosions. This leaves an excess of negative charge on one of the objects,. what is static electricity? it's energy that travels down a metal wire from the place where it's produced (anything from a gigantic power plant to a tiny. static electricity occurs when charge builds up in one place. static electricity, form of electricity resulting from the imbalance between positive and negative charges within a material that occurs when electrons (the negatively.
from www.slideserve.com
what is static electricity? basic principles of electrostatics are introduced in order to explain how objects become charged and to describe the effect. static electricity occurs when charge builds up in one place. The result of an imbalance of this “fluid” (electrons) between objects is called static electricity. Some of the electrons are transferred across. Accumulating a charge requires the transfer of electrons from one object to another. The energy that makes your hair to stand on end can also damage electronics and cause explosions. static electricity can be a nuisance or even a danger. It is called “static” because the displaced. This leaves an excess of negative charge on one of the objects,.
PPT Static Electricity Lessons PowerPoint Presentation ID1608585
Explain Static Electricity It is called “static” because the displaced. what is static electricity? static electricity, form of electricity resulting from the imbalance between positive and negative charges within a material that occurs when electrons (the negatively. The result of an imbalance of this “fluid” (electrons) between objects is called static electricity. basic principles of electrostatics are introduced in order to explain how objects become charged and to describe the effect. static electricity occurs when charge builds up in one place. Typically, objects are neither positively or negatively charged—they experience an overall charge of zero. it's energy that travels down a metal wire from the place where it's produced (anything from a gigantic power plant to a tiny. Some of the electrons are transferred across. The energy that makes your hair to stand on end can also damage electronics and cause explosions. It is called “static” because the displaced. Accumulating a charge requires the transfer of electrons from one object to another. static electricity can be a nuisance or even a danger. This leaves an excess of negative charge on one of the objects,.
From www.nsta.org
Q What Is “Static Electricity,” and How Can I See Its Effects? NSTA Explain Static Electricity static electricity occurs when charge builds up in one place. It is called “static” because the displaced. This leaves an excess of negative charge on one of the objects,. The result of an imbalance of this “fluid” (electrons) between objects is called static electricity. Typically, objects are neither positively or negatively charged—they experience an overall charge of zero. . Explain Static Electricity.
From in.pinterest.com
Redirecting Third grade science, Teaching science, Science electricity Explain Static Electricity This leaves an excess of negative charge on one of the objects,. it's energy that travels down a metal wire from the place where it's produced (anything from a gigantic power plant to a tiny. static electricity can be a nuisance or even a danger. static electricity occurs when charge builds up in one place. Typically, objects. Explain Static Electricity.
From www.science-sparks.com
Static Electricity Experiments for Kids Science for Kids Explain Static Electricity Accumulating a charge requires the transfer of electrons from one object to another. static electricity occurs when charge builds up in one place. what is static electricity? static electricity, form of electricity resulting from the imbalance between positive and negative charges within a material that occurs when electrons (the negatively. it's energy that travels down a. Explain Static Electricity.
From onceuponacreativeclassroom.blogspot.com
Once Upon a Creative Classroom Electricity and Unit and a Explain Static Electricity static electricity, form of electricity resulting from the imbalance between positive and negative charges within a material that occurs when electrons (the negatively. what is static electricity? The energy that makes your hair to stand on end can also damage electronics and cause explosions. The result of an imbalance of this “fluid” (electrons) between objects is called static. Explain Static Electricity.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT What is static electricity? PowerPoint Presentation, free Explain Static Electricity The energy that makes your hair to stand on end can also damage electronics and cause explosions. Typically, objects are neither positively or negatively charged—they experience an overall charge of zero. The result of an imbalance of this “fluid” (electrons) between objects is called static electricity. It is called “static” because the displaced. Some of the electrons are transferred across.. Explain Static Electricity.
From www.slideshare.net
Static Electricity Explain Static Electricity what is static electricity? it's energy that travels down a metal wire from the place where it's produced (anything from a gigantic power plant to a tiny. static electricity occurs when charge builds up in one place. Typically, objects are neither positively or negatively charged—they experience an overall charge of zero. static electricity can be a. Explain Static Electricity.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT ELECTRICITY PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5469002 Explain Static Electricity The result of an imbalance of this “fluid” (electrons) between objects is called static electricity. Typically, objects are neither positively or negatively charged—they experience an overall charge of zero. basic principles of electrostatics are introduced in order to explain how objects become charged and to describe the effect. it's energy that travels down a metal wire from the. Explain Static Electricity.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Static Electricity Lessons PowerPoint Presentation ID1608585 Explain Static Electricity The result of an imbalance of this “fluid” (electrons) between objects is called static electricity. basic principles of electrostatics are introduced in order to explain how objects become charged and to describe the effect. Typically, objects are neither positively or negatively charged—they experience an overall charge of zero. The energy that makes your hair to stand on end can. Explain Static Electricity.
From www.studypool.com
SOLUTION Igcse physics static electricity Studypool Explain Static Electricity The energy that makes your hair to stand on end can also damage electronics and cause explosions. Accumulating a charge requires the transfer of electrons from one object to another. This leaves an excess of negative charge on one of the objects,. basic principles of electrostatics are introduced in order to explain how objects become charged and to describe. Explain Static Electricity.
From marelyghopforbes.blogspot.com
Static Electricity Is Best Described as Explain Static Electricity It is called “static” because the displaced. static electricity, form of electricity resulting from the imbalance between positive and negative charges within a material that occurs when electrons (the negatively. Accumulating a charge requires the transfer of electrons from one object to another. basic principles of electrostatics are introduced in order to explain how objects become charged and. Explain Static Electricity.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Static Electricity Lessons PowerPoint Presentation, free download Explain Static Electricity Some of the electrons are transferred across. it's energy that travels down a metal wire from the place where it's produced (anything from a gigantic power plant to a tiny. This leaves an excess of negative charge on one of the objects,. static electricity occurs when charge builds up in one place. static electricity can be a. Explain Static Electricity.
From www.slideshare.net
Unit 1 Static Electricity Explain Static Electricity basic principles of electrostatics are introduced in order to explain how objects become charged and to describe the effect. Typically, objects are neither positively or negatively charged—they experience an overall charge of zero. It is called “static” because the displaced. Some of the electrons are transferred across. static electricity can be a nuisance or even a danger. The. Explain Static Electricity.
From pixels.com
Static Electricity On Rubbing Rod With Cloth Photograph by Science Explain Static Electricity Accumulating a charge requires the transfer of electrons from one object to another. It is called “static” because the displaced. The energy that makes your hair to stand on end can also damage electronics and cause explosions. Typically, objects are neither positively or negatively charged—they experience an overall charge of zero. what is static electricity? it's energy that. Explain Static Electricity.
From slideplayer.com
Static Electricity and Charging Objects ppt download Explain Static Electricity Some of the electrons are transferred across. The energy that makes your hair to stand on end can also damage electronics and cause explosions. what is static electricity? It is called “static” because the displaced. This leaves an excess of negative charge on one of the objects,. static electricity can be a nuisance or even a danger. . Explain Static Electricity.
From slideplayer.com
Static Electricity and Charging Objects ppt download Explain Static Electricity static electricity can be a nuisance or even a danger. It is called “static” because the displaced. This leaves an excess of negative charge on one of the objects,. The result of an imbalance of this “fluid” (electrons) between objects is called static electricity. The energy that makes your hair to stand on end can also damage electronics and. Explain Static Electricity.
From www.lusadu.com
STATICELECTRICITYFORMTWONOTES Explain Static Electricity The result of an imbalance of this “fluid” (electrons) between objects is called static electricity. basic principles of electrostatics are introduced in order to explain how objects become charged and to describe the effect. This leaves an excess of negative charge on one of the objects,. it's energy that travels down a metal wire from the place where. Explain Static Electricity.
From www.youtube.com
The science of static electricity Anuradha Bhagwat YouTube Explain Static Electricity Typically, objects are neither positively or negatively charged—they experience an overall charge of zero. static electricity, form of electricity resulting from the imbalance between positive and negative charges within a material that occurs when electrons (the negatively. Some of the electrons are transferred across. what is static electricity? The result of an imbalance of this “fluid” (electrons) between. Explain Static Electricity.
From ceutllss.blob.core.windows.net
Examples Of Static Electricity In Daily Life at Sarah Hernandez blog Explain Static Electricity basic principles of electrostatics are introduced in order to explain how objects become charged and to describe the effect. Typically, objects are neither positively or negatively charged—they experience an overall charge of zero. This leaves an excess of negative charge on one of the objects,. Some of the electrons are transferred across. Accumulating a charge requires the transfer of. Explain Static Electricity.